
28 Mar Definition of VOIP and How Does VOIP Work – 2023
Table of Contents
Introduction
VoIP is a technology that lets users make and receive terminated phone calls. Internet instead of the old-style Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN). VoIP goes by many names: virtual telephony, online telephone systems, cloud-based telephone systems, IP telephony, virtual calling tools, etc.
These terms mean the same thing: instead of using a traditional landline phone for voice calls, VoIP manages phone communication over the Internet.
VOIP Skip to navigation Skip to search. Voice over Internet Protocol is a methodology and group of technologies for delivering voice communications and multimedia conferences over Internet Protocol (IP) networks, such as the Internet.
It positions for “Voice Over Internet Protocol” and often pronounces “VoIP.” VoIP is a telephone connection over the Internet. Data remain sent digitally, using Internet Protocol (IP) instead of analog phone lines.
It would support if you had a computer, an Internet connection, and VoIP software to use VoIP. It would need assistance if you also had a microphone, an analog phone adapter, or a VoIP phone. Many VoIP programs let you use a primary microphone and speaker setup. Others require VoIP phones, just like regular phones, but typically connect to your computer via USB. Analog phone adapters allow you to use regular phones with your computer. IP phones are another option that connects directly to a router via Ethernet or wirelessly. These phones have all the necessary VoIP software and therefore do not need a computer system.
The primary provider of VoIP services is Vonage, but other companies offer similar services. While Vonage cares about a monthly service fee, programs like Skype and PeerMe allow users to connect and talk for free. However, these free services may offer fewer connections, lower audio quality, and less reliable than paid services like Vonage.
VoIP is also known as IP telephony, Internet telephony, and digital telephone.
How does VOIP Work?
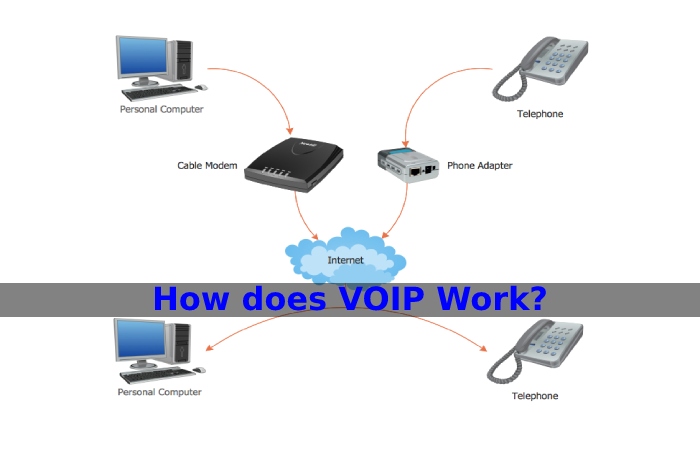
It is made possible by a process called packet switching. This method breaks a sender’s voice data into smaller pieces (called packets) that then download to a router. The packets then forwarded to the recipient’s router before reaching the recipient’s device. Once all remain received, the recipient’s device uses the instructions in each packet to restore the entire message to its original form.
Compressing and decompressing data for transmission involves various audio and video codecs. The specific codec to use depends on the type and size of the data, as well as the transmission’s primary purpose (speed, bandwidth conservation, quality, etc.). Some standard codecs include G.711, G.722, G.729, Speex, and Siren, among many others.
Benefits of VOIP
As mentioned above, VoIP offers several compelling advantages over traditional phone systems. These include:
- Lower Costs – Regardless of how many lines remain needed, It generally requires lower initial and ongoing maintenance costs than traditional phone systems.
- Better scalability – Most [VoIP] service providers allow customers to add or remove users and lines as needed, meaning customers only pay for precisely what they need.
- Mobility – The ability to work from anywhere with an Internet connection is an inherent advantage of it.
- Improved call quality: Although this has not always been the case, It services offer crisp, clear sound quality with minimal latency, dropout, or delay issues.
What is the Equipment Required for VoIP
A high-speed Internet connection remains required and can remain through a cable modem or high-speed services such as a local area network. A specialized computer, adapter, or phone is required. Some it services only work on your computer or a particular it phone. Other services let you use a traditional phone connected to a it adapter. Some software and an inexpensive microphone are desirable if you use your computer. It phones connect directly to your broadband connection and work like a traditional phone. If you use a phone with a it adapter, you can dial as you always have, and your service provider may also provide a dial tone.


No Comments